There are a lot of pathologies of the joints, they vary by origin, development mechanism, symptoms and methods of treatment.Most often, among others, arthritis and arthrosis are diagnosed.The diseases are similar, but have some important differences.Differential diagnosis is necessary for the correct selection of therapy and timely prevention of severe complications.In order to prevent misunderstandings and confusion, you should figure out how arthrosis differs, and what both ailments are.
What is arthritis and arthrosis, how they differ
Arthritis, arthrosis - two different diseases that affect the joints.Despite the consonance of terms, this is not the same diagnosis, and even more so not synonyms.They have both general and various signs, so they should not be confused.
Arthrosis is a degenerative-dystrophic joint pathology, which is characteristic of:
- damage to the cartilage tissue with the gradual involvement of ligaments, muscles, synovial shell, bones in the destructive process;
- non -inflammatory character;
- chronic form of the course;
- It develops locally, without affecting the body as a whole.
Arthrosis occurs mainly in adulthood, after 45 years, in women against the background of aging of the body, the wear of the musculoskeletal system.Occasionally appears in more young due to significant physical exertion, heavy injuries, adverse working conditions.According to the International Classifier, MKB-10, a code of M15-M19 is assigned.
Arthritis is a collective term that includes any joint diseases:
- is inflammatory;
- It proceeds more often in an acute form, turning into chronic;
- affects bone tissue and joint cavity;
- It occurs as a systemic lesion, with the involvement of several articular compounds and target organs at once in the pathological process.
Adults under 40 years old, as well as children, are subject to arthritis.The disease is reversible, successfully treated subject to timely seeking medical help.According to the classifier, ICD-10 has a code M00-14.
Arthritic and arthrose pathologies are often interconnected.Incomplete arthritis with age leads to dystrophic changes in cartilage.In turn, arthrosis during periods of exacerbation is accompanied by inflammation of the tissues.A joint ailment is called arthroso arthritis.
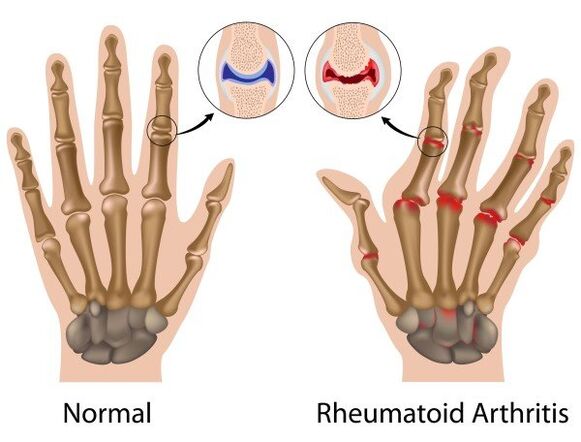
Types of diseases
Arthritis in the official medical classification is divided into species according to several criteria.Depending on the form, acute (severe inflammation, amenable to complete cure) and chronic (incurable pathology with exacerbations).According to the degree of damage to the joints, there is monoarthritis (in one joint), oligoarthritis (in 2-3 joints), polyarthritis (multiple inflammation).
The most popular classifier of arthritis is considered according to the origin:
- rheumatoid - the root cause lies in genetic disorders of an autoimmune nature;
- infectious (septic) - the development of pathogenic microflora directly in the articular cavity;
- reactive - secondary complication of respiratory, genitourinary, intestinal infections;
- traumatic (post -traumatic) - is formed due to mechanical damage to bones, tendons, muscles, ligaments;
- exchange (gouty) - violation of metabolic processes in the body;
- Rheumatic - develops after a bacterial infection in the body.
Arthrosis is characterized by an exclusively chronic form with damage to one articular compound.It affects mainly mobile joints in the human body - legs (knee, ankle, foot), hands (shoulder, elbow), as well as the jaw and vertebral areas.
Depending on the localization, it is divided into:
- knee (gonarthrosis);
- hip (coksartrosis);
- ankle;
- brachial;
- elbow;
- hands;
- thumb of the leg;
- spine (spondylarthrosis);
- cervical (unkwertbral);
- Landing-nomplete (VMS).
Therapy largely depends on the type of articular pathology, especially arthritis.
The difference in the causes of arthritis and arthrosis
Arthritis and arthrosis occur against the background of many adverse factors.The common provocateurs of both diseases are:
- genetic predisposition;
- injuries (bruises, dislocations, subluxation, stretching, fractures);
- congenital anomalies in the development of the musculoskeletal system;
- metabolic and hormonal disorders;
- severe chronic diseases (rheumatism, tuberculosis, diabetes mellitus, thyroid problems);
- improper lifestyle (low activity, poor nutrition, overweight, bad habits);
- Significant physical and emotional loads.
The listed deviations adversely affect the body as a whole, which significantly increases the risk of articular ailment.But there are more direct and obvious causes of each disease separately.
Of great importance in the development of arthritis play:

- infections of viral, fungal, bacterial origin (influenza, salmonellosis, hepatitis, tonsillitis, intestinal infection, Borrell, syphilis);
- autoimmune pathologies (psoriasis, multiple sclerosis, red lupus);
- metabolic violation (gout);
- bone diseases (osteoporosis, osteomyelitis, osteochondrosis, osteoarthrosis);
- allergic reactions;
- low immunity;
- Surgical operations on the joints.
The impetus for the occurrence of pathology can be banal hypothermia, poor sanitary living conditions, an unbalanced diet.
What is the difference between arthrosis and arthritis?Degenerative changes in cartilage for arthrosis, in addition to the listed common causes, occur for reasons:
- age-related disorders of the functionality of the musculoskeletal system;
- unused inflammatory process in the joints (arthritis, synovitis);
- poor blood circulation (atherosclerosis, varicose);
- professional activities (athletes).
Typically, the articular pathology is the result of several internal and external adverse factors at once.
The difference between arthritis and arthrosis in symptoms
The symptoms of two diseases in general manifestations are quite similar.The inflammatory and non -inflammatory damage of the joints is characterized by:
- pain of various intensity;
- a sense of stiffness and stiffness;
- crunch and creak while walking;
- discomfort after prolonged rest;
- painful reaction to weather changes, physical activity;
- External deformation of the affected area.
At the same time, the nature and time of the occurrence of unpleasant sensations, the severity and intensity of the pathological process differ significantly.
By these signs, you can understand what the disease is in front of you - arthritis, arthrosis, what is the difference between them:
- Pain for arthritis occurs suddenly against the backdrop of relative health, with arthrosis, it increases gradually as dystrophic changes in cartilage are progressed - from a couple of months to several years;
- Arthritis painfully bothers at night and morning hours, decreases after joint development, arthrosis pain, on the contrary, subsides at rest and is significantly increased when moving (at the last stage it is constantly present);
- Arthritis is always accompanied by an inflammatory process with swelling, redness, hyperemia, local increase in temperature, for arthrosis, such a course is characteristic only during periods of exacerbations;
- Arthritis is systematic, involving the left and right joints of the legs or arms in the process at the same time, as well as affecting the heart, light, skin, vessels, nervous system.Arthrose lesion usually does not go beyond one pathological joint;
- In the initial stages, the appearance is distinguished - with arthritis, inflammation of the tissues is clearly visible, the place is swollen and becomes hot, with arthrosis there are no visual changes, and only in advanced cases of both diseases does the joint deformation manifest;
- General well -being with arthritis worsens - the temperature rises, there is weakness, malaise, appetite disappears, weight is reduced (in a chronic form this sign may be absent).Such symptoms do not bother patients with arthrosis, only a painful and poorly working joint is in the spotlight.
At different stages of the disease, the clinical picture may vary significantly.It is possible to make an accurate diagnosis only after a complete examination.
Differential diagnosis of arthrosis and arthritis
At the first signs of joint disease, it is necessary to sign up for a consultation with a doctor.An arthrologist is engaged in such pathologies, who knows exactly how to recognize arthritis and arthrosis and what is their difference.If there is no such specialist in the clinic, you can visit an orthopedist, traumatologist, osteopath, rheumatologist, surgeon.With arthritis, depending on the etiology of the disease, an additional consultation of an infectious disease specialist, immunologist, neuropathologist, endocrinologist, cardiologist may be needed.
On the basis of confrontation and initial diagnosis, it is difficult to make an accurate diagnosis.
A number of instrumental research are required:
- radiography to determine the condition of the joints, recognition of injuries, neoplasms;
- CT and MRI for detailed consideration of not only joint cavities, but also soft tissues;
- Ultrasound - is carried out if there are contraindications to x -ray and tomography.
All these methods are quite informative, applicable to both pathologies.
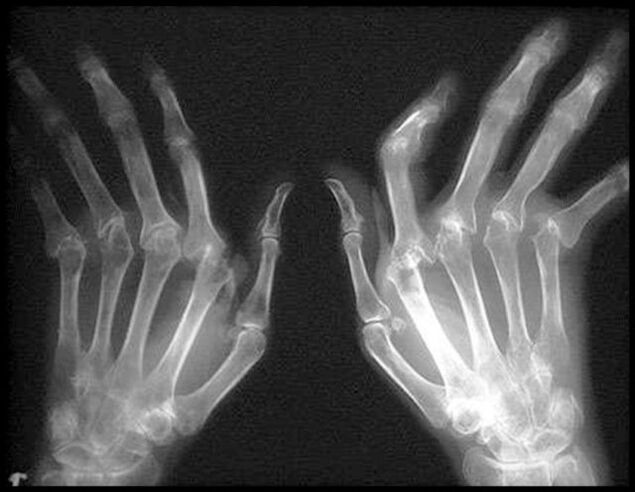
If arthritis is suspected, you can not do without laboratory tests that allow you to identify the root cause of the disease and determine the general condition of the body:
- blood tests for the level of leukocytes, ESR, specific markers;
- urine analysis for uric acid salts;
- rheumatic tests to detect a rheumatoid factor;
- immunological test to assess the state of immune defense of the body;
- PCR diagnostics on the pathogen of infection;
- Arthroscopy for synovial fluid fence for analysis.
A set of methods is selected individually on the basis of a clinical picture and a preliminary inspection of a specialist.A full examination does not take much time, but it is very important for making a differential diagnosis and prescribing suitable treatment.
The difference and features in the treatment of each disease
Both ailments involve special therapy, without which arthritis passes into a chronic form, and arthrosis deprives of performance.
The general principles of treatment are similar, but the tasks are different:
- with arthritis, the main goal is to relieve inflammation, eliminate painful symptoms, prevent complications to other organs;
- With arthrosis, due to the inability to completely cure the disease, the main therapeutic emphasis is on the relief of pain and stopping dystrophic processes in cartilage.
The complex of medical measures necessarily includes medicines in the form of tablets, ointments, creams, solutions, powders, injections.As auxiliary methods, folk recipes, physiotherapy, and therapeutic exercises are used.In advanced cases, you can not do without surgical intervention.
Therapy is selected carefully according to individual indications.There is no universal medicine for arthritis and arthrosis, self -medication is prohibited.
Arthritis and arthrosis - what is the difference in drug treatment
Pharmacy drugs are an integral part of the treatment of both ailments.You can not do without them with arthritis due to the presence of a strong inflammatory process.In therapy they are used:
- Anti -inflammatory non -steroidal drugs in the form of tablets, powders, ointments.Medicines of this group just stop inflammation and concomitant unpleasant symptoms.
- Immunosuppressors.Suppress their own immunity with autoimmune origin.
- Corticosteroid hormones.Select severe pain with a tablet form or intra -articular injections.
- Antibiotics.They have an antibacterial effect in the presence of an infectious process in the body and joint.
NSAIDs and corticosteroids are effective during the period of exacerbation of arthrosis, when inflammation and severe pain are attached to the pathological process.In addition, the disease involves the use of:
- Chondroprotectors to restore cartilage fabric and stop the destruction of the joint.On a long -term basis, powders are used to receive orally, injections intramuscular and intra -articular.
- Oral painkillers.
- Vasodilator drugs to improve blood flow.
- Musorelaxants from hypertonicity and spasming of muscles.
- Vitamin complexes to improve metabolic processes and prevent systemic complications.
Chondroprotective and vitamin agents are also indicated in some forms of arthritis, especially in chronic form.
Correct therapy is selected according to the results of the examination, taking into account the age and well -being of the patient.
Ointment from arthritis and arthrosis
Symptomatic therapy is equally necessary for arthritis and arthrosis of the joints.Various creams, ointments, gels work locally, eliminating inflammation, pain, swelling, discomfort.Moreover, they do not have a systemic effect on the body.
Can alleviate the condition:
- anti -inflammatory ointments based on a special substance;
- other non -steroidal anti -inflammatory drugs;
- painkillers and warming;
- local drugs that improve blood flow and elasticity of the muscle-ligamentous apparatus based on snake and bee venom;
- ointments with shark fat, activating metabolic and regenerative processes in the joints;
- Rubbing with analgesic and anti -inflammatory properties.
Local funds rarely cause side effects, but do not forget about the possibility of a skin allergic reaction.

Traditional medicine
Folk methods are a good assistant in the treatment of arthritis and arthrosis.Home recipes based on natural components have a predominantly symptomatic effect, used as an additional tool.
With arthritic joint inflammation, you can do:
- compresses at night from burdock leaves, white cabbage, aloe, washed in advance and slightly dented to secrete juice;
- Warm baths from pine needles, steaming joints in a healing decoction;
- grinding of a affected place from egg yolk, spoon of apple cider vinegar and turfs of turpentine;
- A herbal decoction of sage, St. John's wort and braids, brewing 2 tablespoons of the collection in a half -leap boiling water, taking 0.5 cups before meals.
To alleviate the condition with arthrosis will help:
- a compress from the root of ginger, grated on a grater and attached to a sore joint to stimulate blood circulation and a warming effect;
- Rubika for the night of 50 g of honey and 1 tsp.healing mummy;
- pepper patch or mustard compress as a thermal procedure;
- Baths based on a decoction of mint leaves or soda-salt solution.
All recipes can be used for both diseases, but only after consulting with the attending physician.Home treatment can help, eliminating unpleasant sensations and harm, causing an allergic reaction and exacerbation.
Exercises for arthritis and arthrosis
The purpose of therapeutic gymnastics is the restoration of joint mobility and the prevention of deformation changes.

To the same way, this task is important for all articular pathologies:
- for the hip area - squats at right angles, swinging legs forward and backward, exercises “bicycle” and “scissors” in the laying position;
- for the knees - sit on the heels from the position on the knees and rise, the exercise “bicycle” - standing standing circular movements of the knees with closed legs, slowly move with a “goose gait”;
- For the ankle - to massage everyone separately a finger, rotate the foot clockwise and against, stretch the sock from you and to yourself;
- for brushes and fingers - make circular movements with a brush in different directions, squeeze and unclench the fist, turn a round object in your hands;
- For the shoulder girdle - to rotate back and forward, raise his arms and shoulders alternately up.
All exercises can only be performed during the remission of the disease by resolving a doctor.
Auxiliary therapeutic techniques
Joint treatment is not limited only to medical and folk methods.It is important to carry out comprehensive therapy, especially at the stage of rehabilitation after an acute period and the restoration of joint mobility.
Experts recommend:
- massage to reduce pain and develop the affected joint (point, honey, manual technique);
- physiotherapeutic procedures in order to improve cell metabolism, accelerate tissue regeneration, complications prevention (magnetotherapy, ultrasound, electrophoresis, paraffinopia);
- alternative medicine (hirudotherapy, acupuncture, kinesitherapy);
- proper nutrition (diet) with a predominance of fruits and vegetables, rejection of harmful foods and alcohol;
- Sanatorium-resort treatment with a full complex of therapeutic services.
In advanced cases, and this often happens with arthrosis, you have to resort to radical surgical methods.Sinectomy, arthroplasty, endoprosthetics, arthrodesis will help the joints to return the joints.Before this state, the course of the disease is better not to allow, performing all medical prescriptions.
Conclusion
We offer in short form information about diseases arthrosis and arthritis, what is the difference in all important criteria:
| Criterion | Arthritis | Arthrosis |
| Etiology | Inflammatory disease, mostly acute form | Degenerative-dystrophic, exclusively chronic course |
| Reasons | Infections, autoimmune and metabolic disorders | Age-related changes in the musculoskeletal system, undercomeengated arthritis |
| Injuries, hormonal failures, large corners, sedentary and unhealthy lifestyle, chronic pathologies | ||
| Symptoms | Sudden appearance, pronounced, there is a common malaise | Gradual growth, symptoms are local |
| Pain, crunch, stiffness, stiffness during walking, external deformation (at the last stage) | ||
| Diagnostics | Laboratory tests of blood and urine | - |
| X -ray, CT, MRI | ||
| Treatment | NSAIDs, corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, antibiotics | Chondroprotectors, analgesics, muscle relaxants, hormones, vitamins |
| Forecast | In most cases, a complete recovery, rarely - the transition to a chronic form | The gradual destruction of the joints, followed by a loss of mobility, disability, the need for surgery |





































